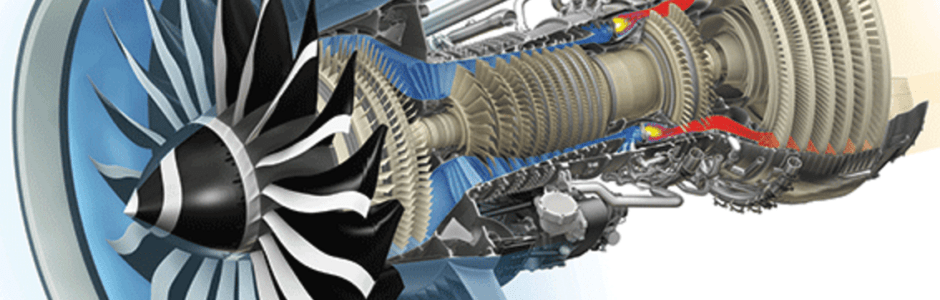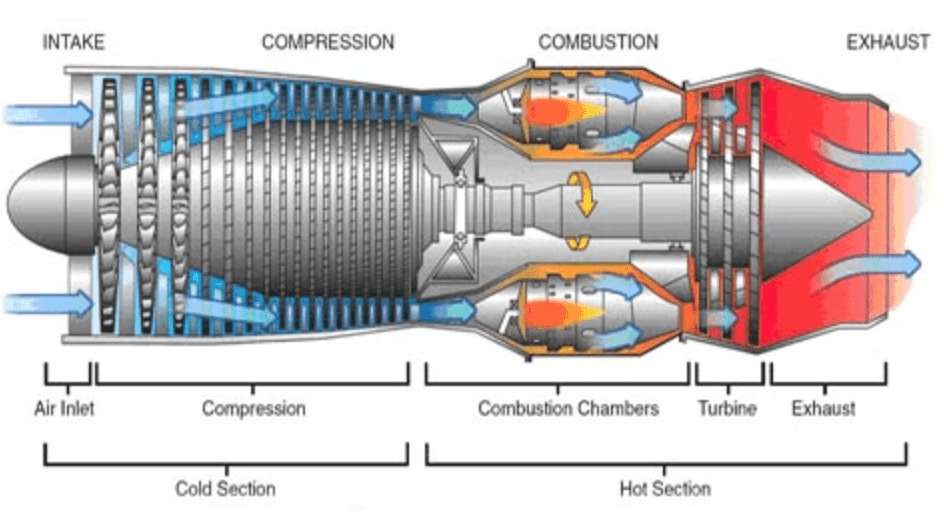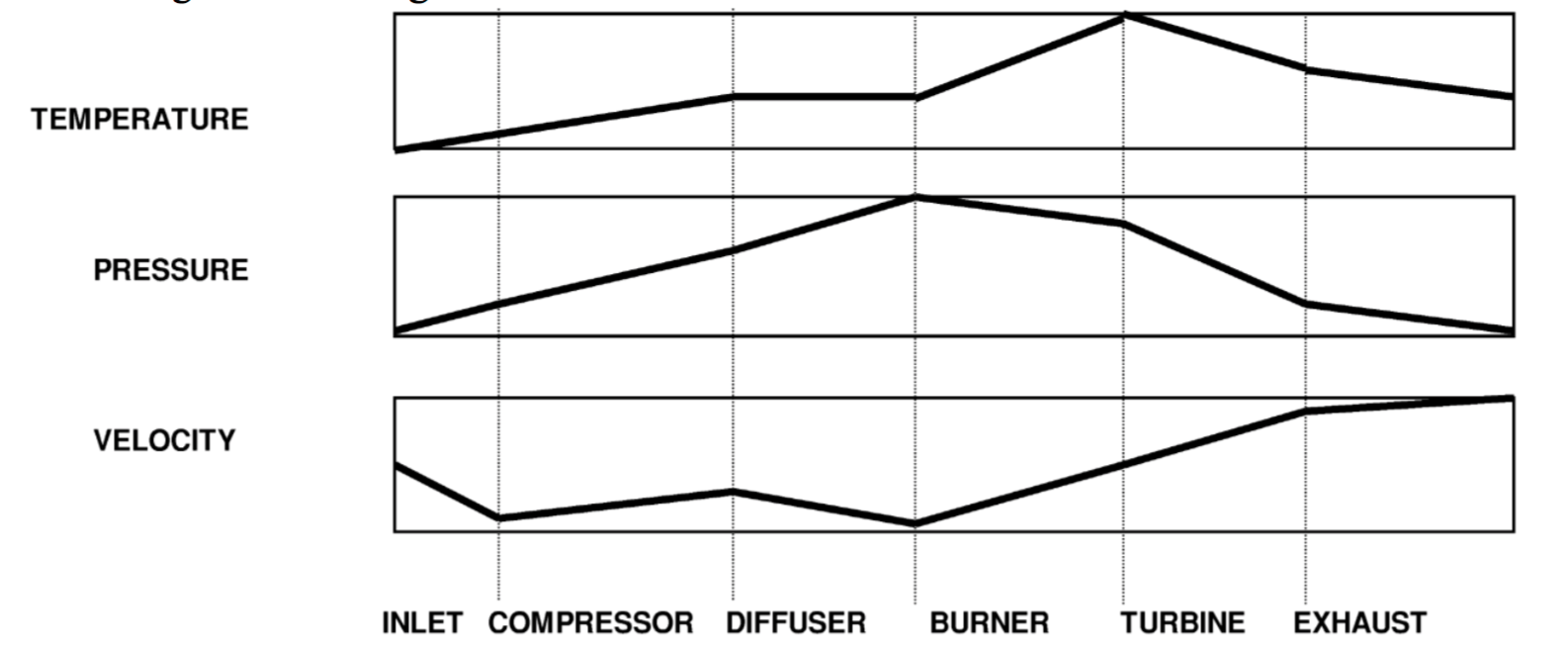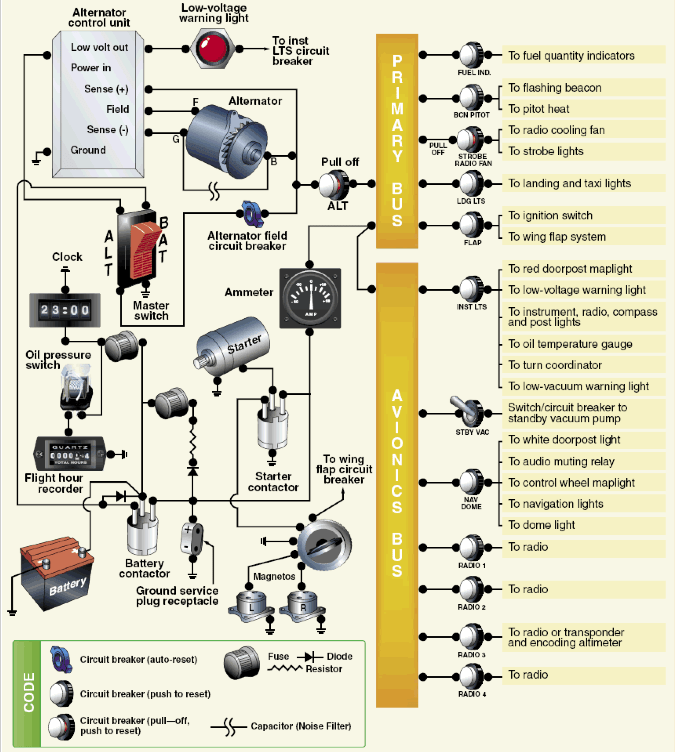
Electrical Systems Review
admin@readysettakeoff.com

Related Articles
-
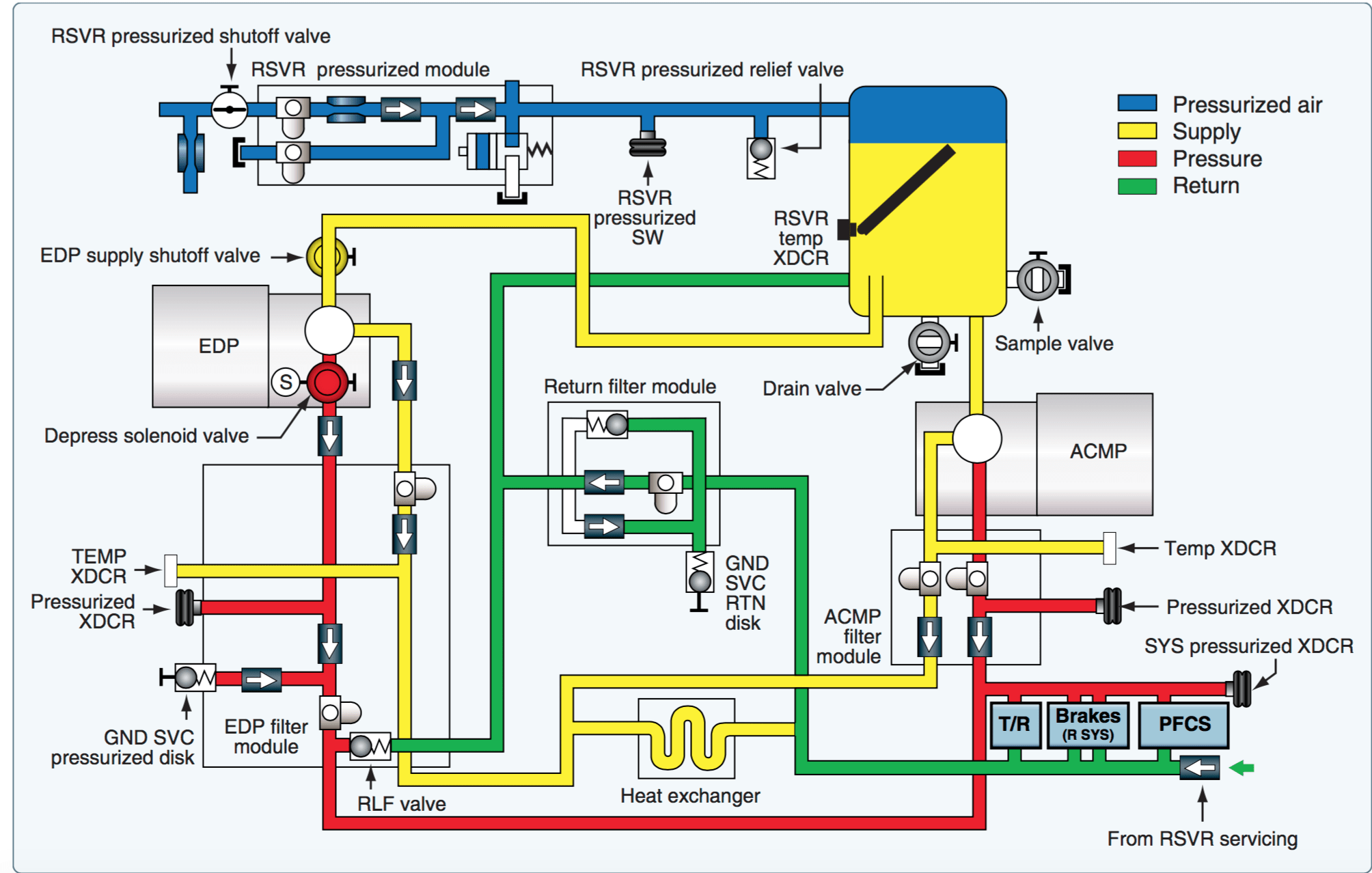
Hydraulic Reservoir
Jet Brain, , Engineering, 0
You are unauthorized to view this page. Please login your credentials Username Password Remember Me Forgot Password
-
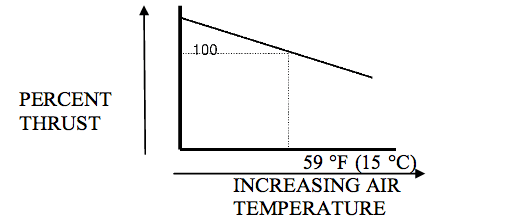
Factors Affecting Thrust
Jet Brain, , Engineering, 0
You are unauthorized to view this page. Please login your credentials
-
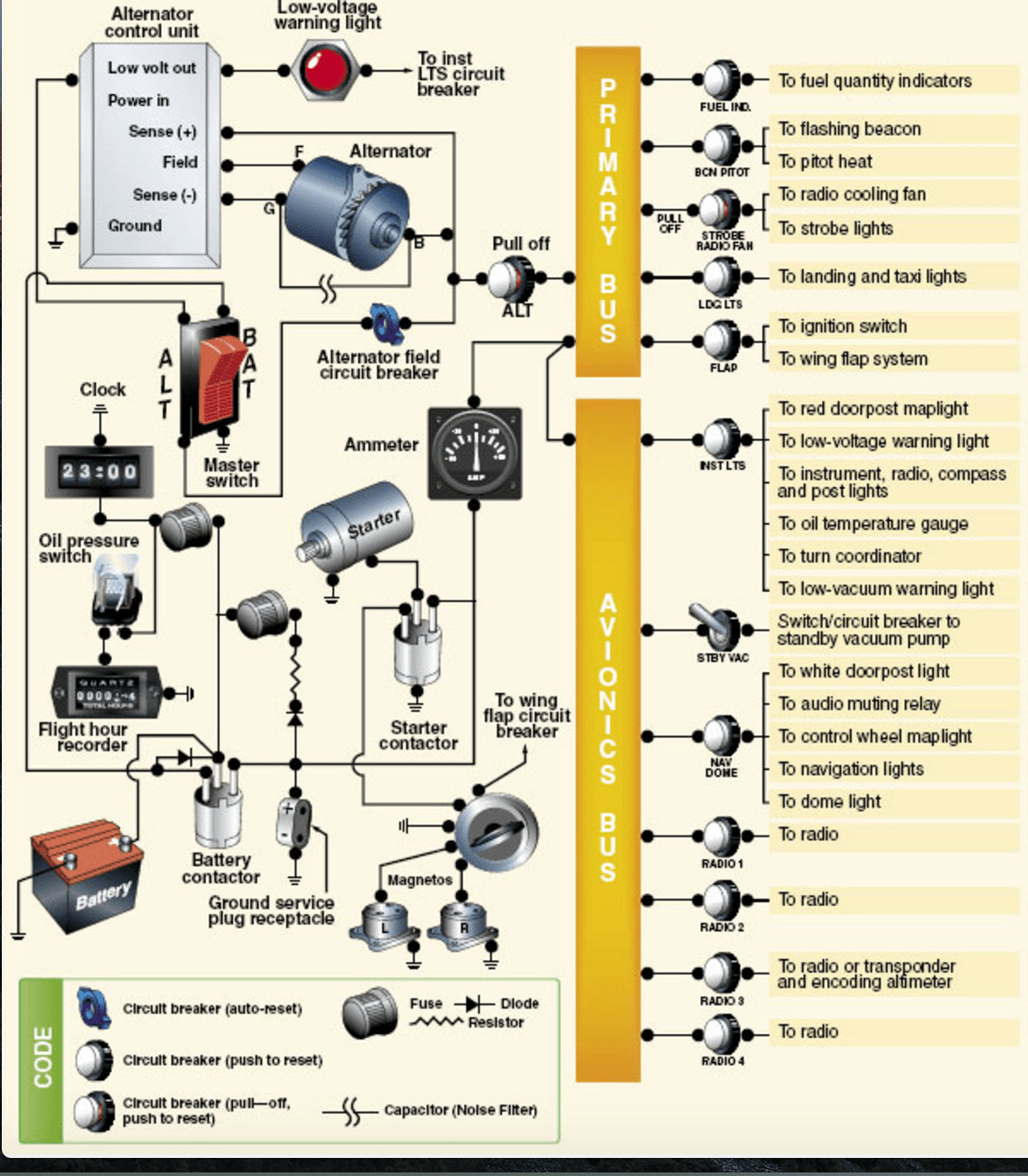
Electrical Systems Review
Jet Brain, , Engineering, 0
You are unauthorized to view this page. Please login your credentials
-
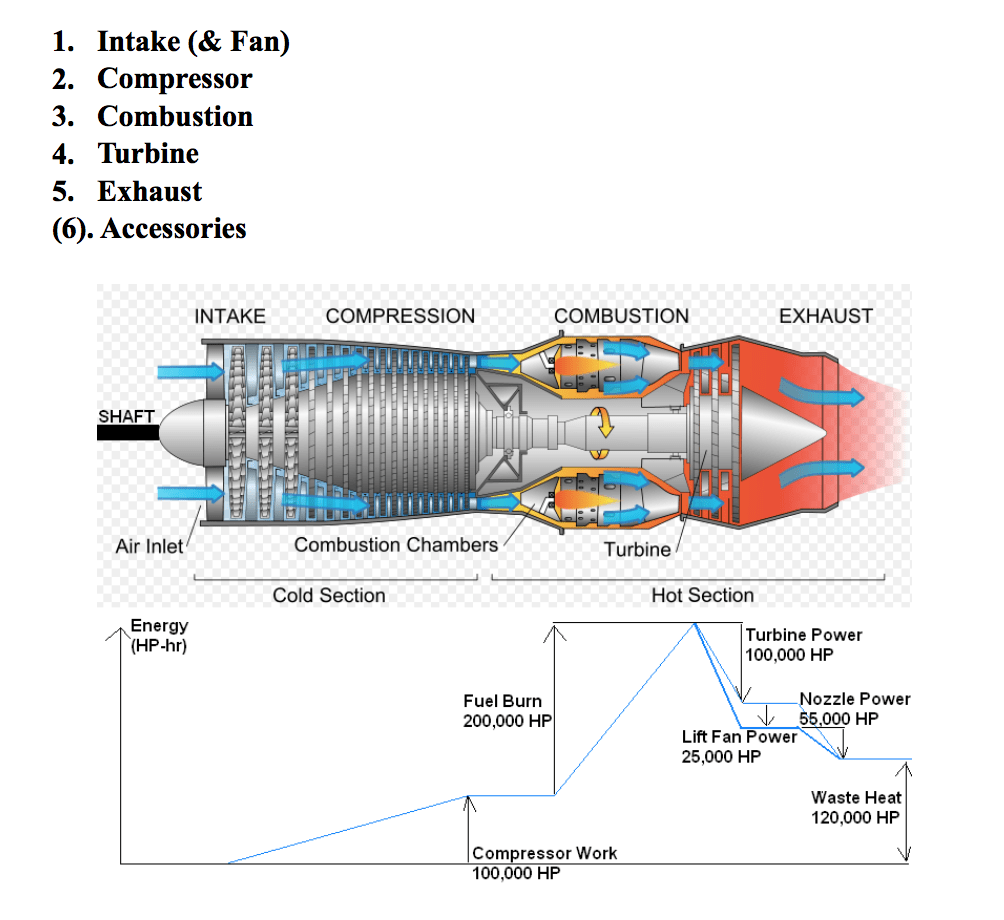
Turbine Engine Review
Jet Brain, , Engineering, 0
You are unauthorized to view this page. Please login your credentials
-
Thermal Efficiency
rstharold, , Engineering, 0
You are unauthorized to view this page. Please login your credentials
-
Compressor Section
Jet Brain, , Engineering, 0
You are unauthorized to view this page. Please login your credentials
-
Turbine Engine/Thrust
Jet Brain, , Engineering, 0
You are unauthorized to view this page. Please login your credentials
-
Constant Speed Drives
Jet Brain, , Engineering, 0
You are unauthorized to view this page. Please login your credentials